class ab amplifier advantages and disadvantages
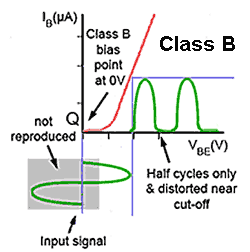
551 but the crossover distortion created by the non-linear section of the transistors input characteristic curve near to cut off in class B is overcome. In the case of Class AB part of the cycle of the input is actually turning the.
Class Ab Amplifiers Electronics Lab Com
Class AB Amplifier.

. From a less than full operational state. A class A amplifier is limited to rather low power levels because its efficiency is so poor. In the second stage i have used Class AB with the resistor biased.
The signal is instantaneously amplified because the tube does not have to wake up. Can be used for much more powerful outputs than class A. The amp will provide a smooth compression because the current is.
After that we can create a pcb circuit and save the gerber file in order to get fabrication. Very low standing bias current. A 30 watt Class A amp can provide louder sound than a Class AB amp with equal power.
With reasonable care in the design it produces the cleanest signal quality. What is Amplifier Classes. Advantages of Class D Amplifiers.
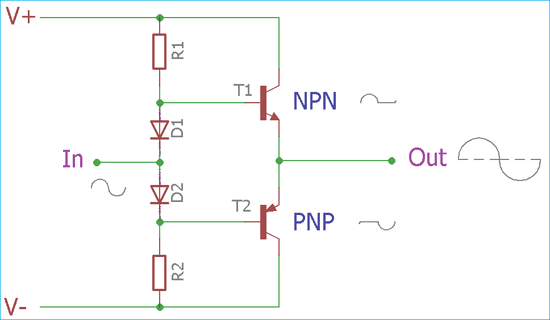
I P i N I Q The constant base voltage condition 2 For example let I Q 1 mA and i N 10 mA. Because current is maximum at all times the amp will. The class AB push-pull output circuit is slightly less efficient than class B because it uses a small quiescent current flowing to bias the transistors just above cut off as shown in Fig.
This extra demand on power supply complexity adds to the cost of class B power amplifiers. Answer 1 of 2. In my point of view class AB audio amplifiers have the following advantages.
In the class D amplifiers there is a low power dissipation. It uses some of the strengths of both Class A and B Amplifiers while also improving on the disadvantages of both categories. Crossover distortion eliminated on Class AB Amplifier.
Its principle of operation is that it is biased in the center of its linear region and is never allowed to sa. Negligible power consumption without signal. To start here is a comparison chart between these two amplifiers Class AB and Class D.
Disadvantages of Class D amplifiers. As a result of the Class B disadvantages the Class AB was developed as a compromise between the two classes. Some methods of biasing voltage biasing diode biasing and potentiometer biasing all present their own advantages and disadvantages.
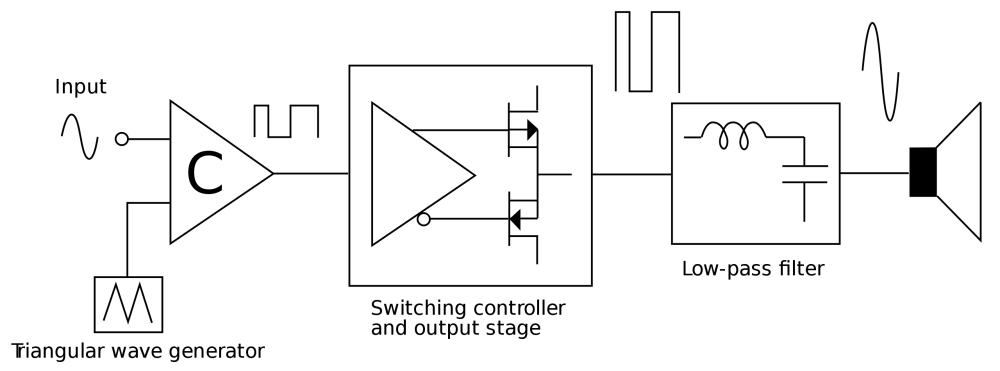
The biggest advantage of a class-D power amp is its high efficiency. The circuit is simple frequency loan small instant distortion. Maximum 80 efficiency can be achieved in radio frequency related operations.
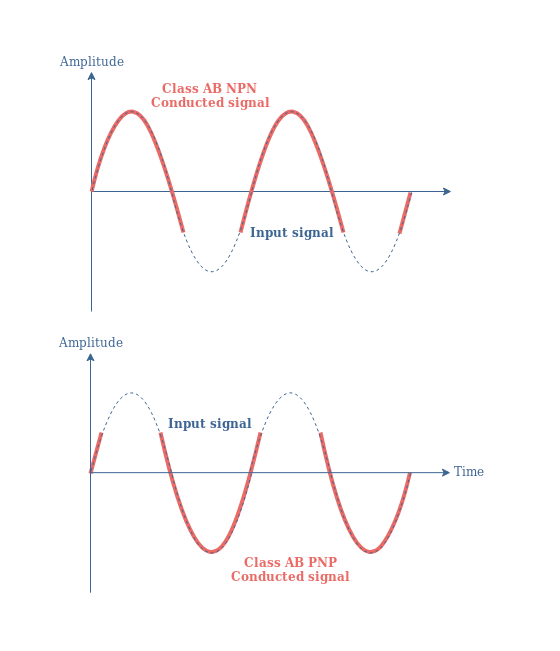
The Class AB amplifier is used in high-fidelity audio systems due to the good signal reproduction and efficiency. The signal is amplified instantaneously because the tune does not need to wake up. I P I Q 2 i N 1106 10103 01mA 1 100 i N The Class AB circuit over most of its input signal range operates as if either the Q N or Q P transistor is conducting and the Q P or Q N transistor.
As the name implies class AB is a combination of class A and class B type of amplifiers. Class A Class BClass ABClass C Class D classes Explained എനതണ ആപലഫയ. Class D Amplifier Advantages.
This chart will help you to understand the clear-cut difference between the. The difference between a Class A and a Class AB amplifier is simply the point at which the transistors are biased. Class D power amplifier speakers may appear distorted for some reason.
Take a look at Figure 3. Class C amplifier uses less than 180-degree conduction angle. The design of the class D amplifier is more complex than the class AB amplifier.
As class A has the problem of low efficiency and class B has distortion problem this class AB is emerged to eliminate these two problems by utilizing the advantages of both the classes. The circuit is very similar to a Class B amplifier with two tubes acting as a push-pull team but this time the tubes stay on a little longer so there is no gap in amplification. First one for the amplification of the Voltage signal Second one for the amplification of the current.
The tube is ready at all times to amplify the signal. Supply current changes with signal stabilised supply. During the initial connection and final shutdown of the power transistor of the Class D power amplifier the potential close to the ground will fluctuate which will increase the noise.
AB Class Amplifiers. These amplifiers are also called as the digital amplifiers. Class C amplifier is tuned amplifier which works in two different operating modes tuned or untuned.
A 30 watt Class A amp will sound louder than a 30 watt Class AB amp. The tube is ready to amplify the signal at all times. Class AB Circuit Operation VTC cont.
The cross over distortion is the problem that occurs when both the. This Class D weigh less than A B or AB amplifiers. Hi-Fi quality sound Simpler design if well designed.
Comparison chart for Class AB Amplifier vs Class D. In the case of Class A the transistor is biased so that over the entire cycle of the RF input the transistor is operating within its linear portion. There is a list of advantages and disavantages of the most common audio amplifiers topologies.
In the sense of hearing the bass is thick the midrange is soft and warm the treble is clear and sharp and the layering is good. The efficiency of Class C amplifier is much more than the A B and AB. Class AB is a union of the two designs for the best of both worlds.
The advantages of Class A amplifiers are no crossover distortion and switching distortion and the harmonic components are mainly even harmonics. Very low distortion THD usually less than 01 at medium output power Linear behaviour. Gain of the non-inverting amplifier is 1 RFR2 where RF and R2 shown in the Image.
It also provides low heat power dissipation incredible performance provides great output and can be utilized for multiple purposes. The class D amplifier has more efficiency that is more than 90. Class AB use two FETs or transistors like in B Class.
The chart highlights the differences in power use heat specs efficiency and ease of use among other relevant comparisons. Class AB Power Amplifiers.

Class Ab Amplifier Design And Class Ab Biasing
What Is The Difference Between Class Ab And Class D Amplifiers Missing Remote

Types Of Power Amplifier Classes Explained In Simple Words Homemade Circuit Projects

Amplifier Classes And The Classification Of Amplifiers

Pdf Amplifier Alphabet Soup Part I Class A Ab B And C

Class Ab Amplifier Circuit Working Advantages Disadvantages

Amplifier Classes And The Classification Of Amplifiers

Amplifier Classes And The Classification Of Amplifiers
Classes Of Power Amplifiers Class A B Ab C D Amplifiers Explained

The Classes And Classification Of Amplifiers And Its Applications

The Classes And Classification Of Amplifiers And Its Applications
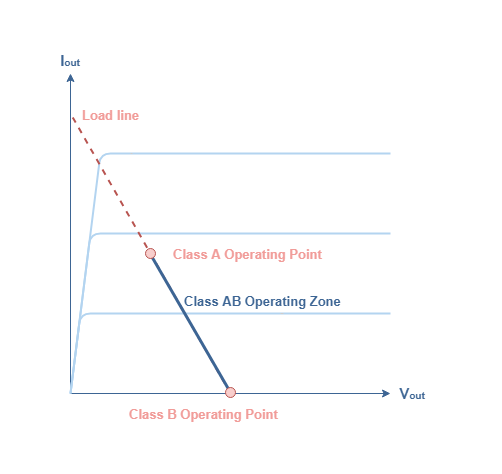
Class Ab Amplifiers Electronics Lab Com

Class Ab Amplifier Circuit Working Advantages Disadvantages
Class B And Class Ab Push Pull Amplifier The Engineering Knowledge

Amplifier Classes And The Classification Of Amplifiers
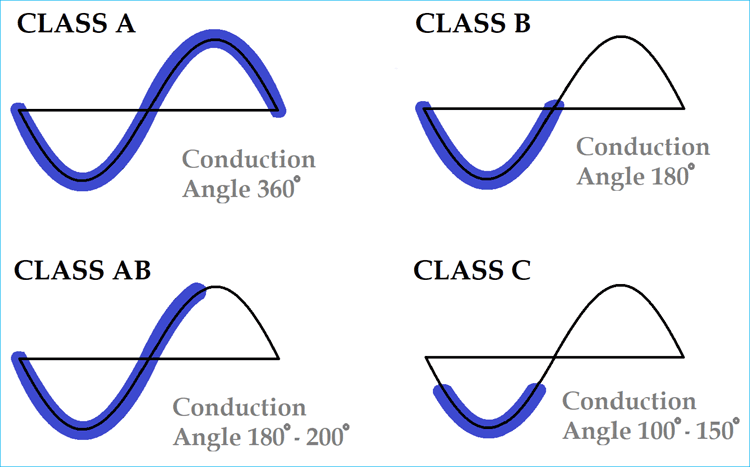
Classes Of Power Amplifiers Class A B Ab C D Amplifiers Explained

Amplifier Classes And The Classification Of Amplifiers
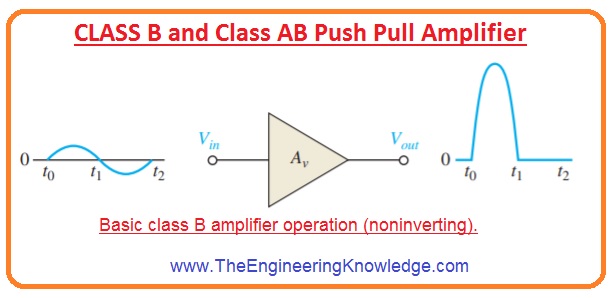
Class B And Class Ab Push Pull Amplifier The Engineering Knowledge